Introduction
Hearing aids have become essential devices for millions of people worldwide, improving their quality of life by enhancing hearing and communication. As demand for hearing aids continues to rise, ensuring consistent product performance and safety is more important than ever. One of the most critical aspects of producing reliable hearing aids is hearing aid quality control. From the selection of raw materials to final product testing, manufacturers must implement strict quality standards to meet regulatory requirements and customer expectations. In this article, we explore the key components of Hearing Aid Quality Control in manufacturing and how companies can maintain excellence in every unit produced.
Raw Material Selection and Component Inspection
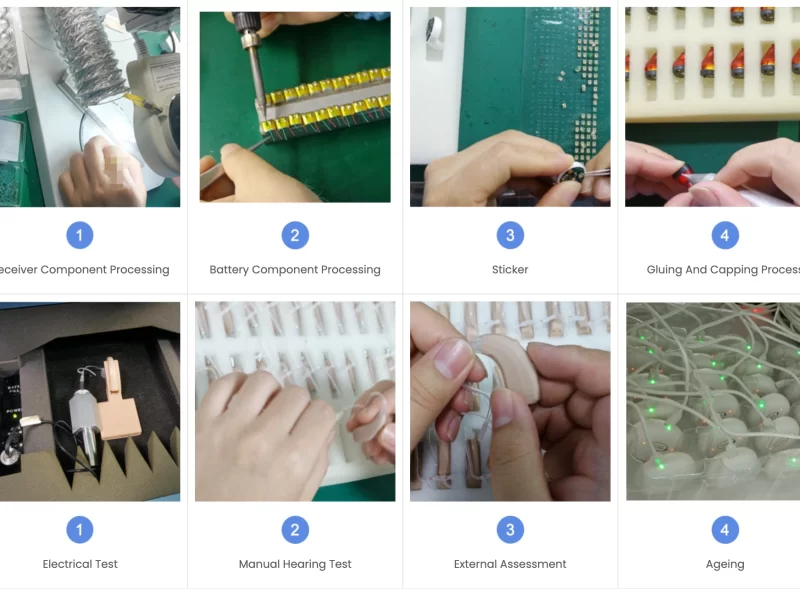
The foundation of hearing aid quality control begins with the careful selection of raw materials and electronic components. High-quality microphones, receivers, and digital processors are essential for superior sound clarity and device longevity. Manufacturers often work with certified suppliers to ensure components meet international standards. For example, a reputable hearing aid factory may conduct batch testing of microchips and batteries before assembly. This early-stage inspection reduces the risk of defective devices entering production, ultimately ensuring that the final product performs as intended. Implementing stringent component verification is a crucial step in achieving reliable Hearing Aid Quality Control.
Assembly Process Monitoring
Once components are verified, the assembly process must be closely monitored. Automated and manual assembly stations are commonly used to build hearing aids with precision. During assembly, technicians perform checks for soldering accuracy, alignment of miniature parts, and proper casing installation. Advanced factories may also employ optical inspection systems to detect microscopic defects in solder joints or electronic circuits. Maintaining strict oversight during assembly not only improves product durability but also ensures consistency across large production batches. Continuous monitoring is a cornerstone of hearing aid quality control, helping manufacturers maintain high standards and reduce warranty claims.
Functional Testing and Performance Evaluation
After assembly, each hearing aid undergoes rigorous functional testing. This phase evaluates sound amplification, frequency response, battery consumption, and feedback suppression. Specialized equipment simulates various listening environments to verify device performance. For instance, a typical hearing aid may be tested for amplification accuracy at multiple frequencies, ensuring it meets audiologist specifications. Data collected during testing helps manufacturers identify potential defects and implement corrective measures before the product reaches consumers. By systematically performing these evaluations, companies reinforce the reliability of their hearing aid quality control process.
Environmental and Durability Testing
Hearing aids are worn daily in diverse conditions, making durability a key aspect of hearing aid quality control. Environmental testing exposes devices to humidity, temperature fluctuations, and dust to confirm their robustness. Shock and vibration tests are also conducted to simulate accidental drops or impacts. A hearing aid that passes these tests demonstrates long-term reliability and user satisfaction. For example, some manufacturers conduct water-resistance tests on moisture-resistant models to ensure compliance with industry standards. Comprehensive durability assessments help manufacturers prevent premature failures and maintain a positive reputation for quality.
Regulatory Compliance and Documentation
Compliance with international standards is another critical component of hearing aid quality control. Manufacturers must adhere to ISO certifications, FDA guidelines, and CE marking requirements, depending on the target market. Proper documentation of inspection results, assembly records, and test outcomes is essential for traceability and regulatory audits. Implementing a robust quality management system allows companies to track deviations, conduct root-cause analysis, and continuously improve production processes. Ensuring regulatory compliance not only protects consumers but also strengthens the credibility of the manufacturer’s Hearing Aid Quality Control practices.
Conclusion
In summary, effective hearing aid quality control in manufacturing encompasses meticulous component selection, precise assembly monitoring, functional and environmental testing, and strict regulatory compliance. Each step plays a vital role in delivering reliable, high-performing hearing aids that improve the lives of users. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can minimize defects, enhance customer satisfaction, and maintain a competitive edge in the hearing aid industry. A comprehensive approach to quality control ensures that every hearing aid leaving the factory meets the highest standards of performance and durability.
ELHearing is a leading hearing aid manufacturer specializing in customizable wholesale solutions. With a commitment to excellence in Hearing Aid Quality Control, ELHearing integrates advanced testing protocols and precise assembly techniques to produce high-quality, reliable devices. Our dedication to quality and innovation ensures that every hearing aid meets rigorous standards and delivers exceptional hearing experiences for users worldwide.
