What are Digital Hearing Aids
Digital hearing aids are sophisticated, technologically advanced devices designed to enhance and optimize auditory experiences for individuals with hearing impairments. Unlike traditional analog counterparts, digital hearing aids use cutting-edge digital signal processing to convert sound waves into precise digital signals. This allows for the customization of amplification, noise reduction, and other essential features to suit the specific needs and preferences of the user.
One of the key advantages of digital hearing aids is their ability to process and differentiate between various frequencies, providing a more accurate and natural representation of sounds. This advanced technology enables users to enjoy clearer speech, improved music perception, and a reduction in background noise for a more comfortable listening experience.
Digital hearing aids often come equipped with programmable settings, allowing audiologists to fine-tune the devices to address specific hearing challenges faced by the individual wearer. Additionally, many digital hearing aids offer wireless connectivity, enabling seamless integration with smartphones and other audio devices for enhanced accessibility and convenience.
The compact and discreet design of digital hearing aids, coupled with their advanced features, represents a significant advancement in hearing assistance technology. These devices play a crucial role in improving the overall quality of life for individuals with hearing loss by providing them with a personalized and effective solution to better engage with the auditory world around them.
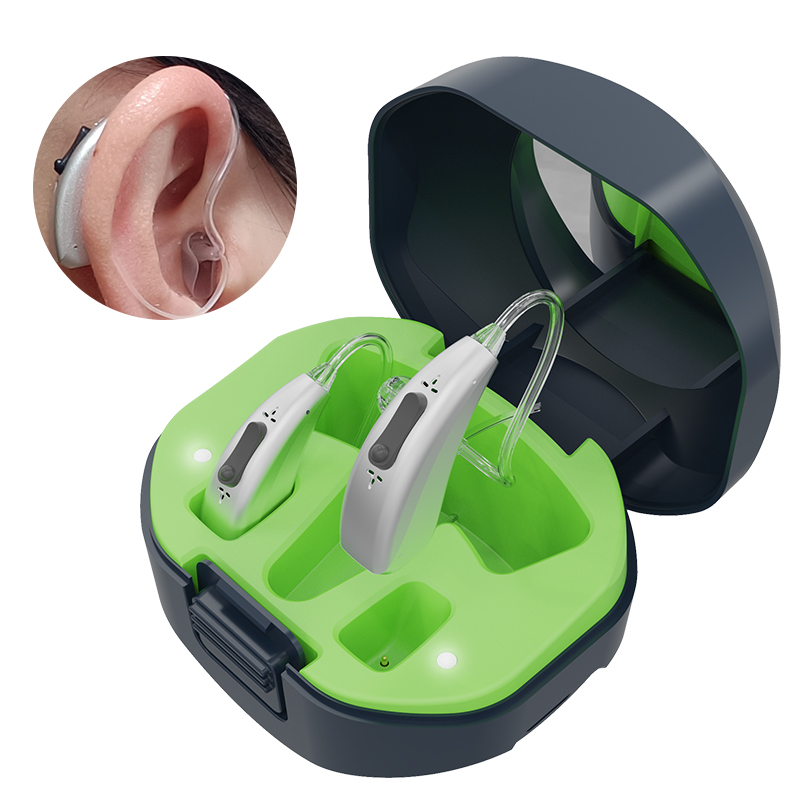
Digital Rechargeable Bluetooth App Control
How do Digital Hearing Aids Work?
Digital hearing aids operate through advanced technology that transforms and enhances auditory signals, catering to the unique needs of individuals with hearing impairments. The fundamental process involves several key components working in tandem to provide a more refined and personalized hearing experience.
1. Sound Reception: The hearing aid consists of a microphone that captures the sound waves from the environment. The sound is then converted into an electrical signal.
2. Analogue-to-Digital Conversion: The electrical signal is then converted from an analogue format to a digital format using an analogue-to-digital converter. This conversion allows for more precise processing and manipulation of the sound signal.
3. Signal Processing: The digital signal is processed using advanced algorithms and signal processing techniques in the hearing aid’s microchip. This processing can include amplification, noise reduction, feedback cancellation, and other adjustments to enhance the clarity and quality of the sound.
4. Digital-to-Analogue Conversion: After the digital signal has been processed, it is converted back into an analogue format using a digital-to-analogue converter. This analogue signal is then sent to the speaker or receiver of the hearing aid.
5. Sound Amplification: The analogue signal is amplified by the hearing aid’s amplifier to a level appropriate for the wearer’s hearing loss. The amplified sound is delivered to the ear canal through a speaker or receiver.
6. Feedback Management: Digital hearing aids are equipped with feedback cancellation systems to prevent the occurrence of whistling or feedback sounds. These systems can identify and cancel feedback before it becomes audible to the wearer. Feedback is when the hearing aid can “hear” itself and makes the high pitched whistling noise, like when you tap a microphone.
7. Additional Features: Many digital hearing aids come with additional features such as Bluetooth connectivity, directional microphones, telecoils (for compatibility with hearing loop systems), and smartphone apps for remote control and customisation.
8.Amplification and Customization: Digital hearing aids can selectively amplify specific frequencies based on the user’s unique hearing profile. This customization is crucial for addressing individual hearing loss patterns and preferences. Unlike analog counterparts, digital aids can amplify relevant sounds while suppressing unwanted noise, providing a clearer and more natural listening experience.

RIC BTE Hearing Aids With Bluetooth
In summary, digital hearing aids combine advanced hardware and software components to process, customize, and amplify auditory signals. This sophisticated technology not only addresses the basic amplification needs but also caters to the diverse and dynamic nature of real-world listening scenarios, ultimately improving the quality of life for individuals with hearing loss.
